buch.ch: Customer Retention in Internet Book Sales
buch.ch AG, a subsidiary of buch.de internetstores AG, sells books, CDs, DVDs, software, and computer games over the Internet. The competition is only a click away and, like buch.ch, meets the high performance and availability requirements of online retail systems. buch.ch recognized at an early stage that it had to distinguish itself from the competition and has already implemented a range of customer retention measures successfully. It operates a Web 2.0 community platform called Alexandria and information about its initial reception in Germany is now available. Alexandria enables customers to create their own personal library, post reviews of books, and index their books using tags (keywords). Whenever readers are looking for new books to read, therefore, they can use the ratings and classifications left by other readers.
table des matières
1. The Company2. What Triggered the Project
E-Shop
3. Customer Retention in Internet Book Sales
Fulfillment, Multi-Channel , Customer Retention, Process Perspective, Application Perspective , ERP , Technical Perspective , VPN
4. Project Flow and Operation
5. Experiences
6. Success Factors
1. The Company
In 1996, buch.ch AG was the first Swiss bookseller to go online. As a department of the Schneebeli AG bookshop, buch.ch grew to become the market leader in Swiss Internet book sales. Since 2001, buch.ch has been a subsidiary of buch.de internetstores AG, 35% of which belongs to the Thalia Holding GmbH corporation. In December 2002, buch.ch took over Internet bookseller bol.ch, whose operations it moved from Munich to Winterthur. buch.ch collaborates with the retail outlets of Thalia (Basel, Bern, Schaffhausen, Spreitenbach, and Thun), Stauffacher (Bern), Meissner BĂĽcher AG (Aarau), and ZAP (Zur alten Post, Brig), which also belong to the Thalia Holding corporation.
The parent company, buch.de internetstores AG, which is headquartered in MĂĽnster/Westphalia, specializes in the online sale of books, music, films, software, and games and also sells electronics and stationery items. With its subsidiary buch.ch AG in Winterthur (Switzerland), it currently operates 18 Web shops in Germany, Austria, and Switzerland. These include the brands buch.de, bol.de, alphamusic.de, and flexist.de in Germany, buch.ch and bol.ch in Switzerland, lion.cc in Austria, and the Web sites of the Thalia bookshops (thalia.de, thalia.ch, and thalia.at).
Background, Industry, Products, and Target Group
The core business of buch.ch is the sale of books, CDs, DVDs, software, and computer games over the Internet. buch.ch has responded to the desire of many people to make more of their purchases over the Internet by continually increasing its product range and enhancing all of its online and offline processes. As the largest online bookshop in Switzerland, buch.ch is one of the fastest in the industry – orders are normally dispatched within 24 hours. In addition to secure, convenient shopping, buch.ch also offers many services such as the option for customers to pick up orders themselves at partner branches, a free gift service, and the ability to pay with UBS KeyClub points or Miles & More miles. buch.ch has also been offering e-books since August 2003.
Importance of IT and E-Business
Further development and operation of dedicated systems is a core competence of buch.de internetstores AG, which invests in the development of custom features to distinguish itself from the competition.
2. What Triggered the Project
Initial Situation and Trigger for the Project
Competition in online book sales is becoming ever fiercer. Booksellers' e-shops are technically advanced and even look similar. buch.ch and buch.de have implemented various internal and external measures to set themselves apart from the competition. These include:
• Fulfillment for several companies
• Customer retention measures
• Alexandria community platform
These measures are described below from a business perspective ("?Business Perspective and Goals"). To keep to the case study framework, the subsequent sections describe the development and processes of the Alexandria community platform.
buch.de and buch.ch are very open to new Web 2.0 technologies. In February 2007, for example, buch.de became the first German bookseller to open a retail outlet, BOL-Mediadome, in Second Life. It then tested various marketing methods such as exhibiting books, handing out vouchers, and holding an avatar competition. buch.de has since ended its involvement in Second Life, since it was unable to identify any promising marketing methods. Nevertheless, the experience provided very valuable insights into customer behavior.
In early summer 2007, buch.de began to develop the Alexandria book community, which is closely linked to its e-shop and allows customers to create their own libraries. The beta version of Alexandria has been in operation since September 2007 and is currently being developed further. The definitive version will also be used by buch.ch. In addition, buch.ch already offers numerous other customer retention measures such as Miles & More, UBS KeyClub, promotional vouchers, and newsletters.
Our Business Partners
Business Software Provider and Implementation Partner
The e-commerce software for the e-shop and the catalog system are provided by freiheit.com technologies GmbH, Hamburg, which develops large, custom software systems for the entire value-added chain in electronic sales – including for booksellers libri.de and books.ch – as well as specific business software based on Internet technologies. freiheit.com offers software that allows companies to set themselves apart from the competition or to resolve specific problems for which no standard software exists.
Advertising Agency
Full-service agency P.AD. Werbeagentur GmbH, with headquarters in Meinerzhagen and Cologne, is responsible for designing the e-shops of buch.ch and buch.de.
3. Customer Retention in Internet Book Sales
Business Perspective and Goals
Fulfillment
buch.ch trades online only. Besides its own-brand e-shops, buch.ch and bol.ch, buch.ch also operates the e-shops for the retail outlets of Thalia BĂĽcher AG, Basel. These include Stauffacher Buchhandlungen AG, Meissner BĂĽcher AG, and ZAP* Zur alten Post AG. buch.ch is responsible for fulfilling all the purchase orders received at the e-shops of the retail outlets.
Exceptions to this are purchase orders for which the customer wishes to pick up the goods at a retail outlet. These purchase orders are filtered out at the order analysis stage and forwarded to the retail outlets. In this case, the traders at the retail outlets are then responsible for procuring the relevant items and further processing the orders.
Collaboration between buch.ch and the booksellers at the retail outlets is contractually regulated and allows the booksellers to pursue a multi-channel strategy without having to run their own e-shop. Marketing measures such as the layout and content of the e-shops are defined by the traders at the retail outlets. All of the e-shops use the same catalog data and systems (see Section ?"Application Perspective").
The purchase orders from all the e-shops are transferred to the inventory management system of buch.ch, where they are processed according to date of receipt regardless of the e-shop in which they were placed (see Fig. ?1). The customer service desk responds to customer queries from all e-shops and is responsible for the overall ordering process and requirements planning.
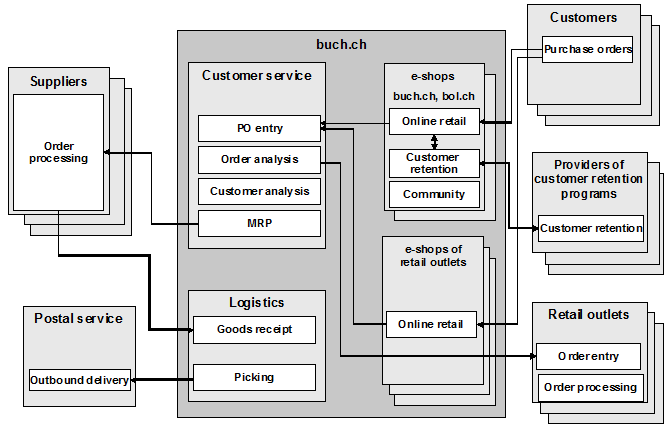
Fig. 1: Business Scenario: Fulfillment and Customer Retention at buch.ch
buch.ch obtains the items from wholesalers such as Buchzentrum AG and Koch, Neff & Volckmar GmbH, but also counts small, specialist distributers among its suppliers. The wholesalers deliver their items in standard containers, each of which holds between 30 and 50 items, and buch.ch groups the purchase orders with this in mind. Purchase orders that, for example, arrive at Buchzentrum AG before 5 p. m. are delivered on the following working day. The invoices (which include the logos of the various e-shops) are printed in the logistics department for each container. The logistics employees must then assign the invoices to the items in each container. The packaged items are picked up and delivered by the postal service twice a day.
buch.ch has 9 customer service employees and 14 logistics employees. Since buch.ch does not have its own warehouse, relatively few staff are required for the fulfillment processes.
Customer Retention
buch.ch has implemented customer retention measures both online and offline. The online measures include community programs such as Miles & More (M&M) and UBS KeyClub.
M&M is the customer retention program of SWISS/Lufthansa. Members of the M&M program can earn points from M&M partners by purchasing products, booking flights, or buying miles. They can then use the miles to buy products from M&M partners. At buch.ch and buch.de, customers receive points for each purchase at a fixed rate. If, for example, a customer buys a book for CHF 99, he or she receives 99 miles. Customers can also pay with miles. The "spend miles" that M&M members use to pay for goods at buch.ch are refunded to buch.ch by M&M. The "earn miles" that buch.ch customers receive for their purchases are bought from M&M by buch.ch.
Customers must store their M&M number in the e-shop once only, after which they receive miles automatically for each new purchase. Customers can also sign up to the M&M program directly on the buch.ch Web site, which also benefits M&M. M&M already has 750,000 members in Switzerland.
buch.ch and bol.ch are the exclusive M&M partners in Swiss book retail. buch.ch enjoys a significant advantage over its competitors by participating in the program. Around 10% of customers use M&M. The partnership with M&M is supported by various promotional offers. For example, a triple miles offer is run three times a year in the M&M newsletter. This means that for a certain period of time, customers receive three times as many miles for each purchase.
Besides M&M, buch.ch is also a partner of the UBS KeyClub, the customer retention program of UBS, which has approximately 500,000 members in Switzerland. Members can pay with USB KeyClub points in the e-shop and take advantage of exclusive members-only offers.
Newsletters are used as an additional online customer retention measure. A standard newsletter is sent to customers once a week and special interest newsletters up to three times a week. Special interest newsletters are used, for example, to advertise new works by certain authors. Recipients for these newsletters are selected based on their transaction history. As a result, only those customers who have already purchased books by the same author or on a similar subject receive a special interest newsletter about a new publication.
buch.ch runs regular offline campaigns by including vouchers and product flyers in customer deliveries. The vouchers can be used as of a minimum order value of CHF 50 and are assigned a code based on which the voucher campaigns can be evaluated. Between 10 and 15% of vouchers are used.
Alexandria
The Alexandria community platform is another customer retention instrument. It enables customers to manage their media (books, DVDs, CDs, games, and so on) in personal libraries. Customers can freely assign keywords to their media, thereby creating an unlimited collection of keywords (folksonomy). This folksonomy provides customers with an alternative way of accessing the items in the e-shop. They can use keywords and items to quickly identify community members with similar interests and discover new items in their libraries. The community members also enter information about themselves, their favorite author, or their preferences and post reviews of items. The community thereby creates a huge data basis that can be used to improve existing customer retention measures such as product recommendations and personalized newsletters.
Process Perspective
This and the following sections focus on the Alexandria community platform.
Alexandria is integrated in the buch.de e-shop. Visitors use the homepage of the e-shop to access Alexandria, where they can view the libraries of other community members. The process for creating and extending a library in Alexandria is described below (see Fig. ?2).
Visitors to the e-shop can create their own library. Existing customers can use their customer login details and add the library to their existing customer account. The customer can give his new library a name and decide whether to add the items he has already purchased, those on his personal wish list, or those for which he has posted a review. Users who do not have a customer account can create one. To do this, they need only specify an e-mail address, user name, and password. As soon as a library has been created, the customer can add items and assign keywords. These keywords are referred to as tags (labels).
An unlimited number of tags can be assigned to each item. Tags are visualized as a cloud in the personal customer library, whereby frequently used tags are highlighted. The users can freely define the terms they assign as tags. Blacklists are used to exclude undesirable terms from the tag function. Tags are used in many ways. The tags most frequently assigned by customers are displayed as an overall tag cloud on the Alexandria homepage (see Fig. ?3).
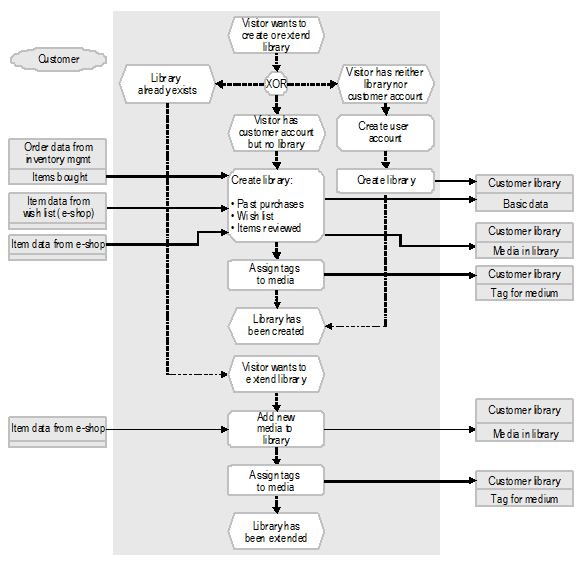
Fig. 2: Process Perspective, Alexandria
The terms in the cloud are links to a separate tag view (see Fig. ?4) that also contains a tag cloud of related tags.

Fig. 3: Tag Cloud

Fig. 4: Tag View for "Fantasy" Tag
The tag view also shows items that have been assigned the tag in question and libraries in which the tag has been used.

Fig. 5: Tag Cloud at Item Level
The tags assigned to a particular item are shown in the e-shop at item level immediately next to the product recommendations ("customers who bought this item also bought..." (see Fig. ?5). The tags are also displayed in a tag cloud with the frequently assigned tags highlighted.
Alexandria users can also assign five different statuses to an item in addition to tags: I own this, I'd like this, I'm reading this now, I've read this, I've lent this. These statuses are also public. If a library in Alexandria has enough items, the user is shown libraries that contain similar items. Users can extend their libraries without limit by searching for items in the e-shop and adding them to their libraries.
Application Perspective
Fig. ?6 shows a highly simplified view of the information systems at buch.ch.
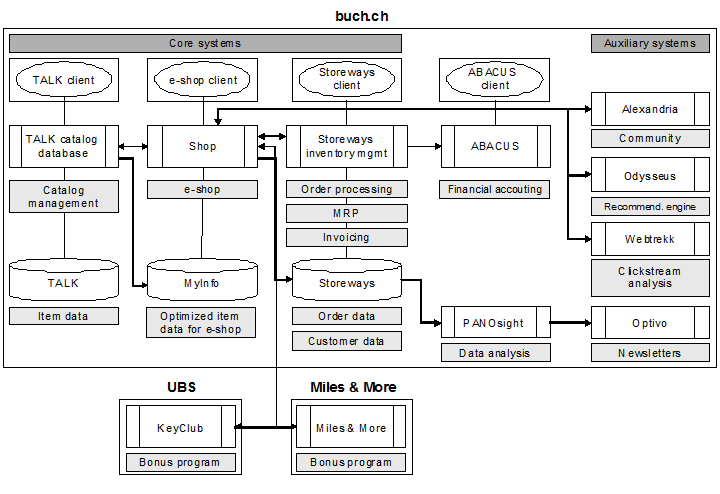
Fig. 6: Application Architecture at buch.ch
The core systems are the TALK catalog system, the e-shop system, and the Storeways inventory management system. The e-shop system and TALK were developed by freiheit.com. Storeways is a custom development of buch.de internetstores AG. Numerous supporting systems are also deployed in addition to the core systems. Fig. ?6 shows a selection of the systems used for customer retention. All brands of buch.de internetstores AG, including those of buch.ch AG and of the booksellers at the retail outlets, are modeled as clients in the core systems. This client capability enables all parties to use the same systems.
Core Systems
buch.ch obtains item data from various data suppliers. Some of this data originates from the catalogs of the book suppliers, but some is purchased from specialist data suppliers. The first phase (genesis) involves matching the item data from approximately 15 data sources. For an item such as the sixth Harry Potter book, for example, the end result of the first phase is a single data record containing all the raw data such as the suppliers, prices, and product images. The aggregated item data forms the basis for the second step (catharsis), in which the item data is refined. A complex ruleset that selects suitable attributes (supplier, price, product data) for each client was developed to refine the item data. This refined item data is then optimized for use in the e-shop and exported to the MyInfo database of the e-shop system. On an average day, TALK processes several thousand updates that are transferred to the database of the e-shop. An update could, for example, be notification from a supplier that an article can no longer be delivered. Breakdowns of the catalog system inevitably lead to the item data in the e-shops being outdated.
The e-shop system of buch.de/buch.ch is based on a redundant server landscape. A load balancer is used to distribute customer queries among several Apache Web servers, which in turn can access several databases. This ensures the availability of the entire system even if individual components fail.
Storeways is the modular ERP system of buch.ch and is used to carry out the following processes:
• Customer and order analysis: Incoming orders are examined and classified. Orders from customers with conspicuous characteristics such as several unpaid invoices are subjected to a manual credit check. Orders that require manual processing, for example, due to a special request by the customer, are also filtered out.
• Requirements planning with purchase order management: Purchase orders are generated for the orders at the suppliers. Purchase order management is used to group the sales orders into suitable mass purchase orders for the suppliers.
• Communication module: The purchase orders are transferred by means of various interfaces. Responses from the suppliers are processed. A response can be a PO confirmation, rejection, or notice of receipt (that is, notification that the purchase order has been received but cannot be processed until a certain point in time). A purchase order may need to be replanned.
• Goods receipt module: Goods receipts are monitored and posted.
• Invoicing and receivables management take place in Storeways.
• Output management: Storeways forwards figures to Financial Accounting and outputs various statistics.
buch.ch uses ABACUS for financial accounting and accounts payable accounting, while SAP software is used in Germany.
Auxiliary Systems for Customer Retention
The customer libraries and item keywords (tags) are stored in the Alexandria database, to which the e-shop system has direct access.
buch.ch uses the Odysseus recommendation system developed by freiheit.com. This is also connected to the e-shop system by means of direct database access. The similarity between items is calculated on an ongoing basis based on customer transactions (item-based collaborative filtering). Items that customers buy together are assigned a high similarity rating. These item similarities are grouped into pools and are available to the e-shop on separate servers. When the customer calls up an item in the e-shop, the system recommends products that show a high degree of similarity to this item.
The PANOsight data analysis software developed by Panoratio Database Images GmbH is used to evaluate the transaction data of the Storeways database. The results of analyses based on customer groups are used, for example, as a basis for sending newsletters.
buch.ch uses the broadmail newsletter software developed by Optivo to send newsletters. For the special interest newsletters, PANOsight and manual queries are used to select groups of customers who belong to the target group of a specific newsletter based on their transaction history. The software can be used to create newsletter campaigns and evaluate customer response using criteria such as number of newsletters opened, number of clicks on content, and other feedback (responses, bounces, autoresponders). If the customer uses a link in the newsletter to access the e-shop, a ProvID is transferred that Storeways can use to track the purchase orders that were generated as a result of the newsletter.
buch.ch uses the Webtrekk software developed by Webtrekk GmbH to analyze customer behavior in the e-shop. The items that a customer clicks during a visit to the e-shop are grouped in sessions and can be used as a basis for item recommendations.
Technical Perspective
Most of the systems used by both buch.ch and buch.de – the e-shop system, TALK, Storeways, Alexandria, Odysseus, and the associated databases – are operated at an external data center. buch.ch has an Internet connection with a dedicated line. The systems on the servers at the data center are maintained by buch.de. buch.ch has access to the servers at the data center by means of a VPN connection (see Fig. ?7).
buch.ch's internal servers run on the Windows and Linux operating systems. The Web servers run on Unix.
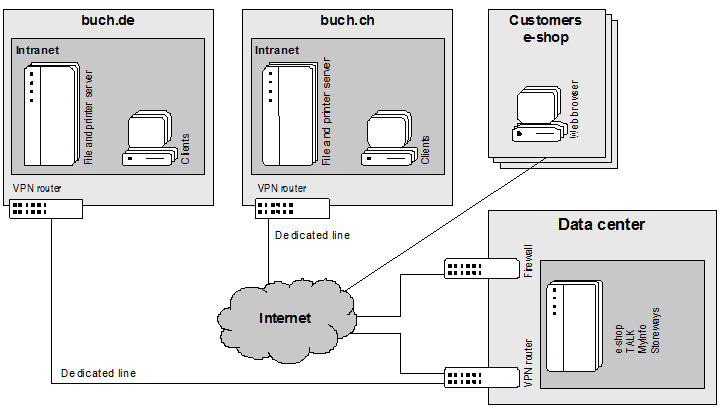
Fig. 7: Technical Perspective, buch.ch and buch.d
4. Project Flow and Operation
Project and Change Management
The investment decision to develop the Alexandria community platform was made by the Executive Board of buch.de internetstores AG. The Head of Purchasing at buch.de assumed responsibility for project management. The actions of the development team were monitored by the project manager in conjunction with other employees of buch.de. The project was very complex. The high level of integration of the community functions with the e-shop and product catalog posed particularly complex requirements for system development. The operation of Alexandria must not affect the performance of the existing e-shop.
Partner Selection
freiheit.com is a long-time partner of buch.de internetstores AG, and was chosen as the partner for the Alexandria project because it was already familiar with the existing systems, which were essential to the complex integration of Alexandria in the e-shop system. The templates were developed by the advertising agency P.AD. This meant that another argument against developing Alexandria with a third party was the increased coordination effort that would be required to collaborate with three partners.
Development and Rollout of the Software Solution
After the internal project planning phase, freiheit.com was commissioned to develop Alexandria. In the first step, a test system was developed that was tested internally by buch.de employees. Authorized buch.de employees used a bug fixing system to report errors and improvement proposals to freiheit.com. These error messages were processed successively by freiheit.com. The beta version of Alexandria was published in the e-shop of buch.de in September 2007, just in time for the book fair.
The existing beta version is being enhanced with community functions that allow members to communicate with one another. Alexandria users will soon be able to exchange private messages. Members can use a shoutbox, which is similar to a pinboard, to leave messages, comments, etc. in the library of another user. Users will also soon be able to create groups. Alexandria users with similar interests can form groups in which to communicate (for example, crime novel groups, cooking groups, and so on). Information will be exchanged using shoutboxes, a type of mini forum within the individual groups. Each community member can create a group and invite selected members to join it or open it to all Alexandria users. A widget, which is a mini application based on JavaScript and Ajax, will enable users to integrate their Alexandria libraries in their own Web sites or blogs. This allows Alexandria users to show on their own blogs which books they have just bought or which books on a certain subject they would recommend.
5. Experiences
Alexandria currently comprises 583 libraries containing 18,815 items. The items have been assigned 7,732 tags (as at 2008-07-06). Users can give feedback on the beta version directly on the Alexandria Web site using a feedback loop or by e-mail. buch.de mainly received positive feedback from users. Alexandria is very popular among existing customers. It is hoped, however, that Alexandria will attract new customers in addition to the existing ones. The target number of users has not yet been reached, therefore. The current number of users is satisfactory in light of the fact that the beta version of Alexandria was only advertised on the company Web site and within the scope of the 2007 book fair.
As soon as the final version of Alexandria goes live, it will be advertised aggressively. An attempt will be made to address the community scene specifically, attract community experts, and obtain their feedback. Existing customers will be informed by newsletter about the final version of Alexandria, which has not been done so far. The beta version of Alexandria was also discussed in the press and criticism was leveled at the lack of community functions to enable users to communicate [Roebke 2008]. Developing a community is difficult to control, since it is not a good idea to be overly paternalistic to members. Alexandria offers users a great deal of freedom, which so far has not been abused.
The Alexandria project has raised awareness at buch.de of a new type of user and changes to customer behavior in the e-shop.
6. Success Factors
Special Features of the Solution
Alexandria is special because it integrates a book community in the e-shop of a commercial retailer. In other book communities such as LovelyBooks [www.lovelybooks.de] and LibraryThing [www.librarything.com], commercial partners, if at all present, tend to remain in the background and are not mentioned explicitly, a fact that was the subject of much discussion at the start of the project. It is too early to say definitively how the marriage of e-shop and online community will affect user acceptance.
Reflection of the "Competitive Advantages"
No comparable communities or e-shops exist. buch.de customers can take advantage of the added value of the community. With Alexandria, buch.de and buch.ch can position themselves as a brand that shares expert knowledge of books and brings together everything to do with books and media on a single platform. User behavior indicates what is important to the customers in the e-shop and for marketing, making it possible to plan and control marketing measures more specifically.
Lessons Learned
The Alexandria project shows that a community platform must be developed in conjunction with employees and customers so that it can meet the needs of its users. The development of a community is a very dynamic process that requires openness to criticism and the willingness to give community members a lot of freedom when using the platform.
buch.ch AG
Ines Bohacek Rothenhäusler, Geschäftsführerin
Secteur: Commerce de gros et de détail
Taille de l'entreprise: Moyen entreprise

buch.de internetsores AG
Bettina Althaus, Leiterin Unternehmenskommunikation
Secteur: Commerce de gros et de détail
Taille de l'entreprise: Moyen entreprise


